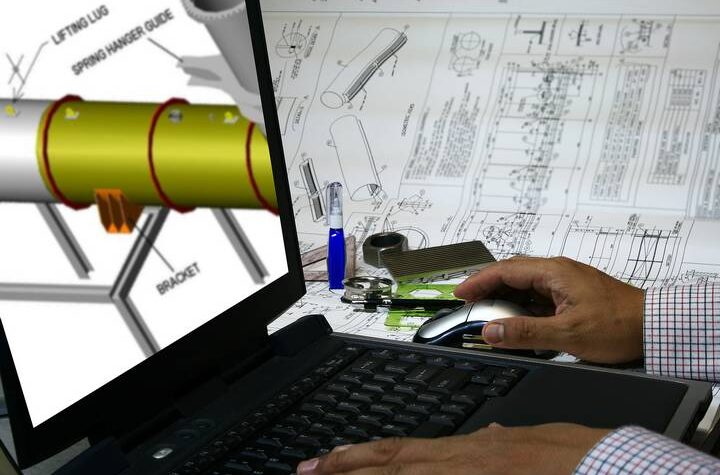
CAD, aka computer-aided design, uses geometrical parameters to create three-dimensional computer models. These models typically represent a system, a part, or a design that can be easily altered by modifying the parameters set. CAD allows designers to openly design products, objects, and models, view them under different representations and analyze them under various parameters. CAD also allows these models to be tested under simulated real-work conditions.
All of this is what makes computer-aided design so valuable in modern design. Here is more about how CAD works.
Who Uses CAD?
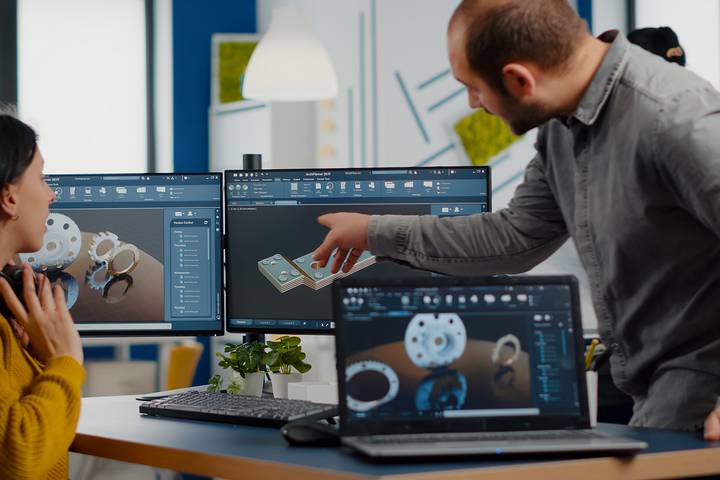

Individuals from various walks of life can use CAD design automation. It is most used by land surveyors, civil engineers, project managers, and construction professionals to design and test various materials, products, objects, and scenarios.
Common CAD Applications
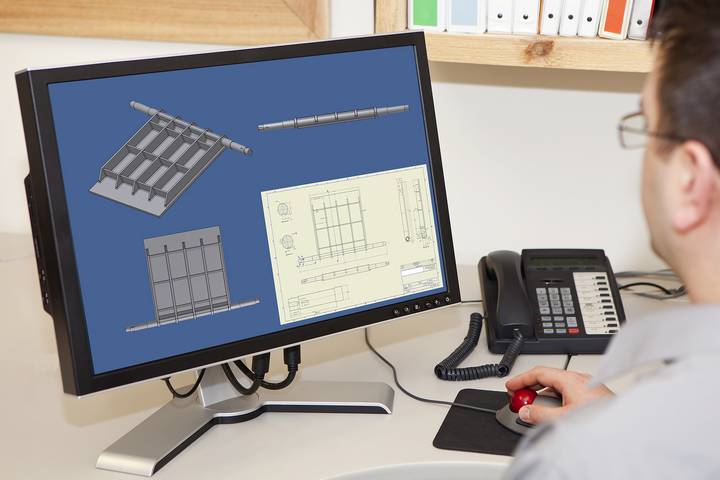

When CAD is talked about or undergoes CAD training, it is often about any of the following four applications.
To design buildings.
Professionals in building design will use CAD to test architecture, construction, and structural engineering.
To create 3D models of infrastructure projects.
Infrastructure engineers use CAD to create life-like designs of infrastructure relating to land development, transportation, utilities, water, or wastewater facilities.
In manufacturing.
CAD models are designed and used commercially to fabricate, print, inspect, and quickly make high-quality parts.
Commercial product design.
CAD creates consumer products, machinery, and equipment in the product development cycle.
How CAD Design Process Works

Traditional drafting and design from decades ago involve using rulers, squares, and compasses. It was time-consuming and highly inefficient compared to how CAD works today. The same work can be performed but without any erasing or redrawing. All a designer has to do is change the parameters to suit whatever instruction they want to provide the object.
The CAD design process can be divided up into multiple stages, beginning with recognition of need and up through to presentation.
Plan.
A recognition of need must occur, demonstrating either a problem that requires corrective action or a hypothesis for a design that requires testing.
Define the design specifications, including physical and functional characteristics and operating performance.
Synthesize.
Plan and implement a product design based on the specifications outlined.
Analyze.
The prior object design is subject to analysis. This often leads to improvements in the design and optimizations based on what is found in close analysis.
Evaluate.
Evaluate the design against the specifications set and whether it fulfills the initial recognition of need.
Unlike if you were building it by hand, CAD has no limits. Designers can construct anything they like and make it anything they wish. This allows someone to pursue creativity with no bounds, maximizing innovation and following the pursuit of ideas with the development, modification, and optimization of design. In short, one improves design quality in a big way with how CAD works.
Types of CAD Design Software
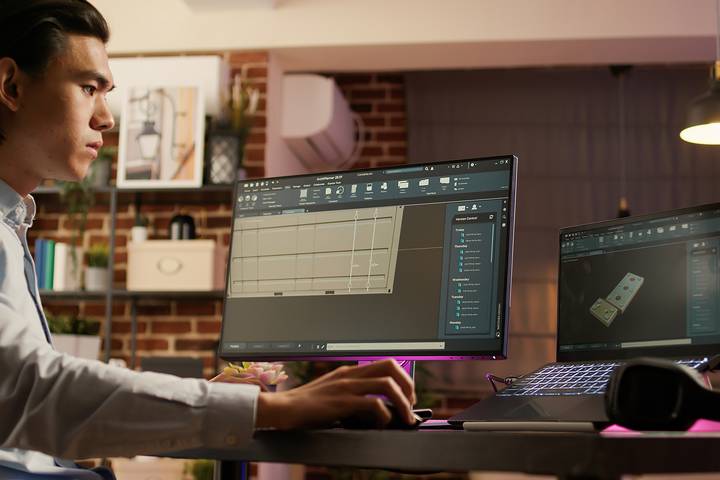

CAD is done through specific software. There are various CAD programs, and some paid and some unpaid, varying in quality and features. The most popular, by far, is AutoCAD which offers 2D and 3D CAD design.
Revit is another type of CAD software that targets building planning, designing, and construction with its Building Information Modeling. Civil 3D is also an option for CAD software, targeting civil engineering design and construction documentation.
Benefits of CAD
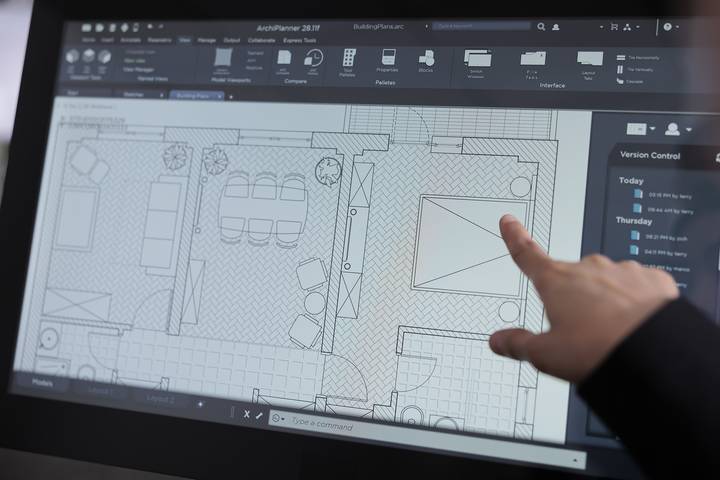
CAD comes with numerous benefits:
CAD Allows You to Inspect The Object From Every Angle
CAD software lets you zoom in, similar to a camera lens. Elements of an object can be magnified and inspected. Most CAD products are three-dimensional, so a designer can rotate them on an axis, providing a fuller view of the object.
As modifications are made to the parameters, this inspection work is necessary to ensure the product is functioning as predicted.
CAD Allows You to Test the Object in Performance
A major aspect of using CAD is performance testing. A common test is a stress response. For example, a system or part is put onto a grid that distorts under a simulation of physical or thermal stress. This can demonstrate the function of a product or material, such as if one is trying to test a building prototype.
Through the stress response, parameters can be modified to test various designs for the purpose assigned.
CAD Allows You to Perform Many Different Tasks
A part of the reason why CAD is so widely used in industries as diverse as bridge construction to movie animation is because of the tasks you can perform with this software.
You can make a 3D model of any design, apply any material or effect to it, and document the aesthetic, function, and performance. It’s a way to test objects in a real-life context without spending the time, effort, and money to make them in real life.